I want the USA government to pay farmers to Grow Hemp and here is how it can be done!
Farmers can split the cost of growing Hemp with the Govt when it's used for #Phytoremediation one example is the FSA Assistance: Cost-share of up to 50%...
information on the Conservation Reserve Program and how Hemps great phytoremediation abilities could play a role in lessening chemical run off from farm fields...Eligible Practices Cost Share Assistance CRP progr...
ELIGIBLE PRACTICES: FOR THIS SIGNUP THE LAND MUST BE ELIGIBLE AND SUITABLE FOR ANY OF THE FOLLOWING CONSERVATION PRACTICES:
Conservation Reserve Program
Farmers can split the cost of growing Hemp with the Govt when it's used for #Phytoremediation one example is the FSA Assistance: Cost-share of up to 50%...
information on the Conservation Reserve Program and how Hemps great phytoremediation abilities could play a role in lessening chemical run off from farm fields...Eligible Practices Cost Share Assistance CRP progr...
ELIGIBLE PRACTICES: FOR THIS SIGNUP THE LAND MUST BE ELIGIBLE AND SUITABLE FOR ANY OF THE FOLLOWING CONSERVATION PRACTICES:
- Filter Strips
- Denitrifying Bioreactor on Filter Strips
- Saturated Filter Strips
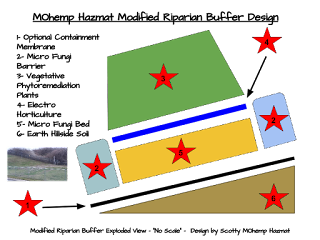
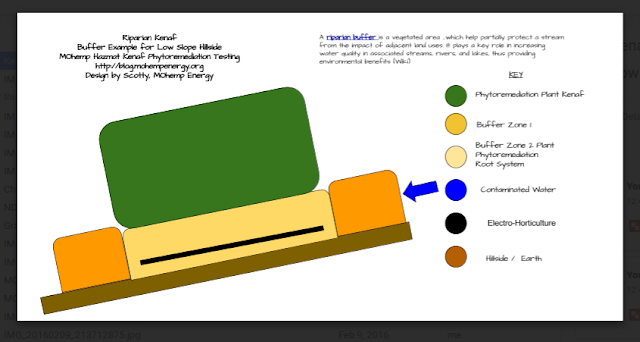
- Riparian Buffer
- Denitrifying Bioreactoron Riparian Buffers
- Saturated Riparian Buffer
Cost-Share Assistance: Cost-share of up to 50 percent of the re-reimbursable cost of installing the practice is provided by FSA.Conservation Stewardship Program. Your Stewardship Goals. Our Assistance
Conservation Reserve Program